How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate surveying missions. Mastering drone operation requires understanding its mechanics, adhering to safety protocols, and respecting legal regulations. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers and troubleshooting, ensuring you’re prepared for a safe and successful flight experience.
We’ll explore the fundamental components of a drone, explaining their functions and interactions. You’ll learn to navigate the controls confidently, execute various maneuvers, and appreciate the importance of pre-flight and post-flight procedures. We’ll also address essential safety considerations, legal compliance, and effective maintenance strategies. By the end, you’ll be well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly and effectively.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the different parts of your drone and the terminology used is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the key components and define common terms used in the drone world.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone is comprised of several essential components working in harmony. Each plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the intricacies of controlling the drone itself, and for a comprehensive guide, I recommend checking out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Proper training ensures safe and effective drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust needed for lift and movement. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust, efficiency, and noise.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. The motor’s power and speed directly influence the drone’s performance.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” processing data from various sensors (gyroscopes, accelerometers, GPS) and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands.
- Battery: Provides the power source for the motors and other electronic components. Battery capacity (measured in mAh) directly affects flight time.
- GPS Module: Allows the drone to determine its location, enabling features like autonomous flight, return-to-home (RTH), and geofencing.
- Radio Transmitter/Controller: This is the remote control used to pilot the drone, sending commands to the flight controller.
- Camera (if applicable): Captures images and videos, offering aerial perspectives. Camera quality varies significantly depending on the drone model.
Glossary of Common Drone Terms
Familiarizing yourself with these terms will greatly enhance your understanding of drone operation and maintenance.
- mAh (milliampere-hour): A measure of battery capacity.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mounting system for the camera, reducing image shake.
- Geofencing: Setting virtual boundaries for the drone’s flight area.
- RTH (Return-to-Home): An automated function that returns the drone to its starting point.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude during flight.
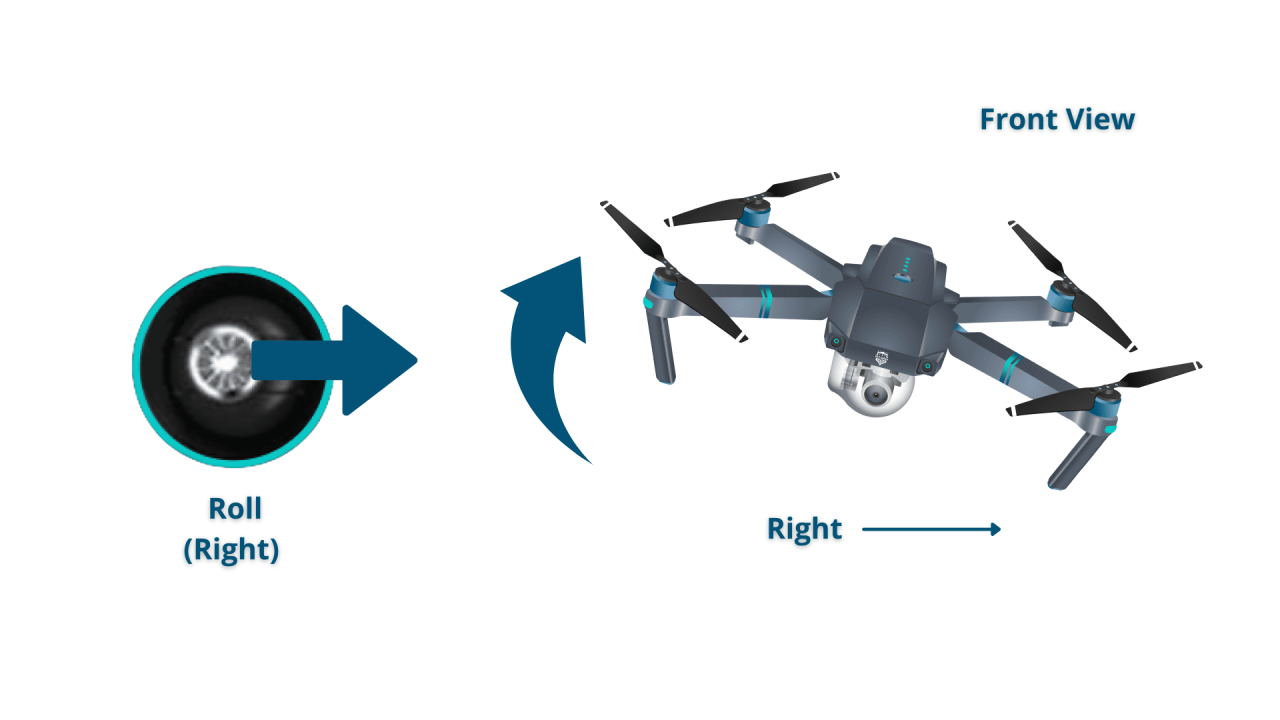
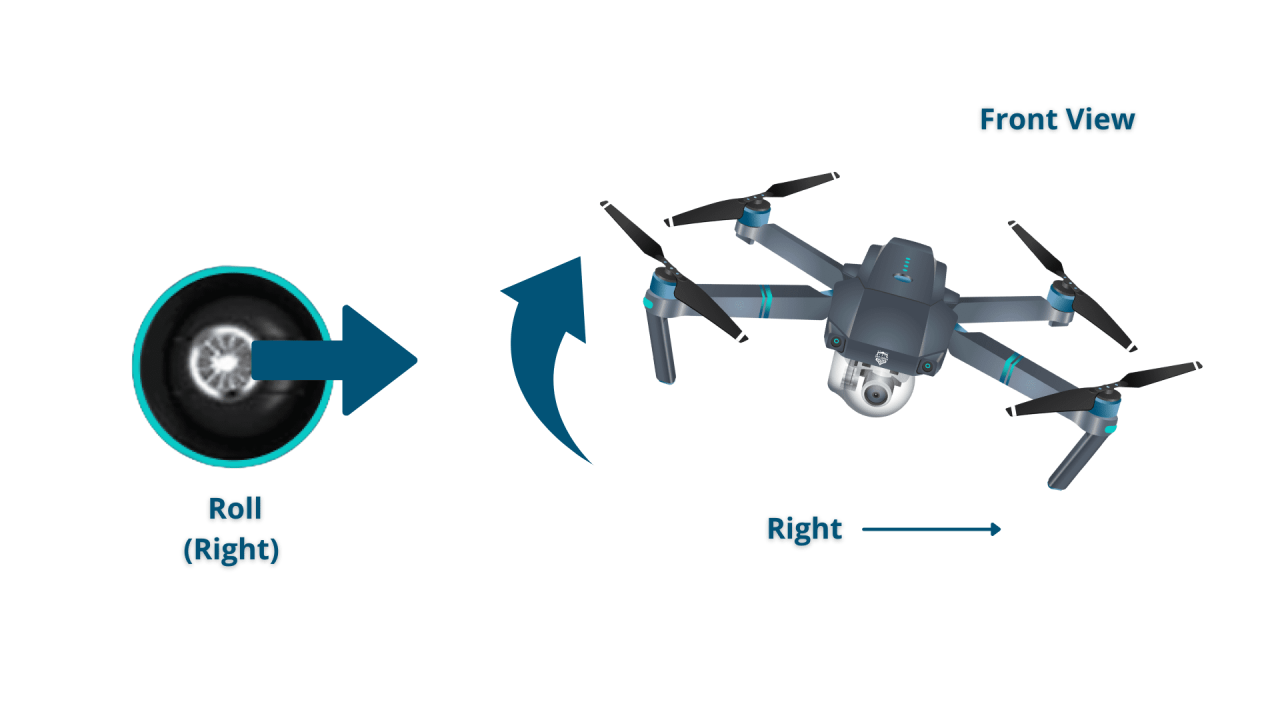
- Yaw, Pitch, Roll: The three axes of rotation for a drone (yaw is rotation around the vertical axis, pitch is rotation around the lateral axis, and roll is rotation around the longitudinal axis).
Drone Propeller Comparison
Different propellers are designed for various purposes, affecting flight characteristics.
| Propeller Type | Thrust | Efficiency | Noise Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| High-Thrust | High | Lower | Higher |
| Slow-Spin | Lower | Higher | Lower |
| Folding | Medium | Medium | Medium |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety guidelines are paramount for responsible drone operation. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, carefully follow this checklist to ensure your drone is ready for safe operation.
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Check battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Inspect the drone’s body for any damage.
- Check the radio transmitter’s battery level.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Plan your flight path and ensure you have sufficient clearance from obstacles.
Drone Safety Guidelines, How to operate a drone
Responsible drone operation requires strict adherence to safety protocols. These guidelines ensure both the safety of the drone and those around it.
- Always fly within visual line of sight (VLOS).
- Avoid flying near airports, crowded areas, or restricted airspace.
- Be aware of surrounding obstacles and avoid collisions.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Always have a backup battery and plan for unexpected situations.
Safe Drone Launch and Landing Procedure
This flowchart Artikels the steps for a safe launch and landing.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal considerations, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become a confident pilot. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation is key to enjoying this exciting technology.
(Note: A visual flowchart would be included here, detailing steps like pre-flight checks, power-on sequence, takeoff, flight maneuvers, landing, and power-off. The steps would be connected with arrows indicating the flow of the process.)
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the basic controls is the foundation for proficient drone piloting. Mastering these maneuvers allows you to safely and effectively control your drone.
Basic Drone Controls
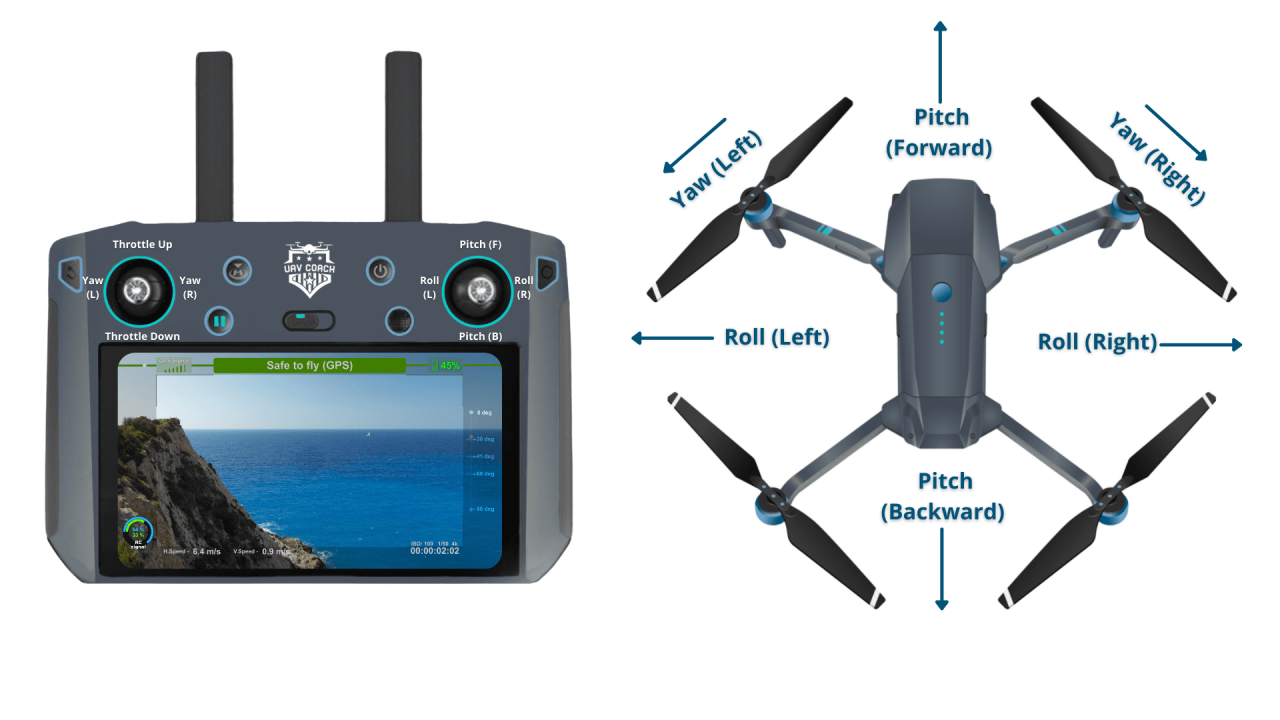
Most drones use a control system based on four primary axes of movement.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude (up and down).
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation (left and right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s forward and backward movement.
- Roll: Controls the drone’s sideways movement (left and right).
Performing Basic Maneuvers
Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting more complex flights.
- Hovering: Maintaining a steady position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude smoothly.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude smoothly.
- Turning: Rotating the drone using the yaw control.
Common Beginner Mistakes
Avoid these common errors to improve your drone piloting skills.
- Ignoring pre-flight checks: Always perform a thorough pre-flight inspection.
- Flying too close to obstacles: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles.
- Using excessive throttle: Fly smoothly and avoid jerky movements.
- Losing visual line of sight: Always maintain visual contact with your drone.
- Ignoring battery level: Monitor battery level and land before it gets critically low.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced techniques to enhance your drone’s capabilities and create stunning aerial footage.
Waypoint Navigation and Filming Techniques
Waypoint navigation allows you to program a flight path, enabling complex maneuvers and automated shots. Advanced filming techniques involve using the drone’s camera settings and movements to achieve desired visual effects, such as smooth panning shots or dynamic tracking shots.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and automation.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS data for stable flight and features like RTH.
- Attitude Mode: Relies on onboard sensors for stability, providing more responsive control but less stability in windy conditions.
Achieving Smooth and Stable Aerial Shots
Smooth aerial shots require practice and a good understanding of the drone’s controls. Smooth, deliberate movements are key to avoiding jerky or shaky footage.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring your drone’s longevity and safe operation. Knowing how to troubleshoot common issues can save time and prevent costly repairs.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Implement a regular maintenance schedule to keep your drone in optimal condition.
- Clean the propellers and drone body after each flight.
- Inspect for damage and wear on all components.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU regularly.
- Store the drone and batteries in a safe, dry place.
- Check and tighten screws periodically.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Addressing common problems quickly can prevent escalating issues.
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, damaged power switch | Check battery, replace battery, inspect power switch | Ensure proper connection |
| Drone is unstable in flight | Low battery, GPS signal loss, damaged sensors | Charge battery, improve GPS signal, check sensors | Calibrate sensors if necessary |
| Motor failure | Damaged motor, faulty ESC | Inspect and replace motor or ESC | Consult repair manual |
| GPS signal loss | Obstructions, interference, weak signal | Find open area, avoid interference, ensure GPS module is functioning | Check for GPS module updates |
Drone Laws and Regulations
Understanding and adhering to drone laws and regulations is crucial to avoid legal repercussions and ensure responsible operation. Regulations vary by region, so it’s vital to research your local laws.
Drone Laws and Regulations by Region
(Note: This section would contain detailed information on specific drone regulations for different countries or regions. Examples would be included for specific jurisdictions.)
Obtaining Permits and Licenses
In many areas, obtaining permits or licenses may be required for commercial drone operations or flights in specific airspace. Failure to obtain necessary permits can result in fines or legal action.
Consequences of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can result in penalties ranging from fines to legal action. Penalties vary depending on the severity of the violation and the jurisdiction.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography, enabling stunning aerial shots. Understanding composition, framing, and camera settings is key to capturing high-quality images and videos.
Basics of Drone Photography Composition and Framing
Apply principles of photography, such as the rule of thirds and leading lines, to create visually appealing images. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to achieve unique shots.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Ensure optimal lighting conditions and use appropriate camera settings (ISO, shutter speed, aperture) to achieve sharp, well-exposed images and videos. Use the drone’s gimbal to stabilize the camera and reduce shake.
Using Different Camera Settings
Experiment with different settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to achieve various effects, such as motion blur or depth of field. Understand how these settings affect the final image or video quality.
Drone Battery Management

Proper battery care is essential for extending battery life and ensuring safe operation. Understanding battery types and charging practices is crucial for optimal performance.
Importance of Proper Battery Care and Storage
Proper storage and handling of drone batteries are crucial for safety and longevity. Avoid extreme temperatures and store batteries in a cool, dry place.
Best Practices for Charging and Discharging
Always use the recommended charger and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and discharging. Avoid overcharging or completely depleting batteries.
Comparison of Different Drone Battery Types

| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) | Flight Time (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S | 1500 | 11.1 | 20-25 minutes |
| LiPo 4S | 2200 | 14.8 | 30-35 minutes |
| LiHV 3S | 1300 | 12.6 | 22-27 minutes |
| LiFePO4 3S | 1800 | 11.1 | 25-30 minutes |
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is vital for safe drone operation. A quick response can prevent accidents and damage.
Handling Various Emergencies
Prepare for potential emergencies, such as loss of signal, low battery, or unexpected malfunctions. Have a plan in place to address each situation safely.
Performing a Safe Emergency Landing
If an emergency arises, prioritize a safe landing. Identify a suitable landing area and bring the drone down smoothly, if possible. If the drone is unresponsive, prepare for a crash landing and prioritize minimizing damage.
Emergency Contact Information and Resources
Keep a list of emergency contact numbers readily available, including local authorities and drone support.
- Local emergency services: [Insert local emergency number]
- Drone manufacturer support: [Insert manufacturer’s contact information]
- Local drone community/forum: [Insert relevant online resources]
Successfully operating a drone is a blend of technical understanding, responsible piloting, and adherence to regulations. This guide has provided a foundational framework, equipping you with the knowledge and skills necessary for safe and proficient drone operation. Remember that continuous practice and ongoing learning are crucial for refining your skills and expanding your capabilities. Embrace the journey, and enjoy the unparalleled perspectives that drone technology offers.
Always prioritize safety and legal compliance above all else.
Helpful Answers
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s sensors?
Calibration frequency depends on usage. Consult your drone’s manual, but generally, recalibration after a significant impact or if you experience erratic flight is recommended.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, immediately try to engage the return-to-home function (if available). If that fails, attempt to manually bring it down safely, prioritizing avoiding people and property. Contact local authorities if necessary.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies widely depending on the model, battery size, and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.